Today I wanted to find what are the international paper sizes.... So hear I thought to let all of you know about it. The sizes will be as below.
The ISO paper size concept
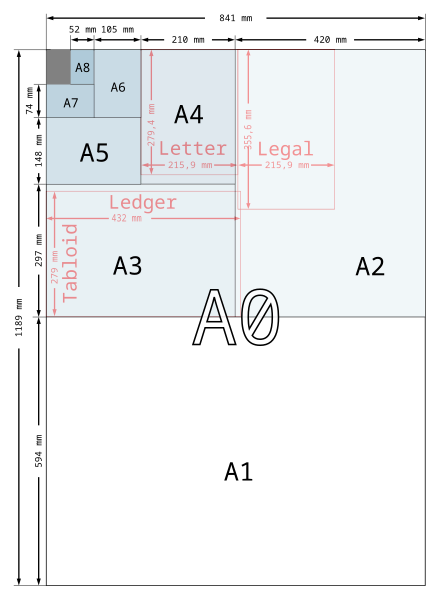
In the ISO paper size system, the height-to-width ratio of all pages is the square root of two (1.4142 : 1). In other words, the width and the height of a page relate to each other like the side and the diagonal of a square. This aspect ratio is especially convenient for a paper size. If you put two such pages next to each other, or equivalently cut one parallel to its shorter side into two equal pieces, then the resulting page will have again the same width/height ratio.

The ISO paper sizes are based on the metric system. The square-root-of-two ratio does not permit both the height and width of the pages to be nicely rounded metric lengths. Therefore, the area of the pages has been defined to have round metric values. As paper is usually specified in g/m², this simplifies calculation of the mass of a document if the format and number of pages are known.
ISO 216 defines the A series of paper sizes based on these simple principles:
- The height divided by the width of all formats is the square root of two (1.4142).
- Format A0 has an area of one square meter.
- Format A1 is A0 cut into two equal pieces. In other words, the height of A1 is the width of A0 and the width of A1 is half the height of A0.
- All smaller A series formats are defined in the same way. If you cut format An parallel to its shorter side into two equal pieces of paper, these will have format A(n+1).
- The standardized height and width of the paper formats is a rounded number of millimeters.
For applications where the ISO A series does not provide an adequate format, the B series has been introduced to cover a wider range of paper sizes. The C series of formats has been defined for envelopes.
- The width and height of a Bn format are the geometric mean between those of the An and the next larger A(n−1) format. For instance, B1 is the geometric mean between A1 and A0, that means the same magnification factor that scales A1 to B1 also scales B1 to A0.
- Similarly, the formats of the C series are the geometric mean between the A and B series formats with the same number. For example, an (unfolded) A4 size letter fits nicely into a C4 envelope, which in turn fits as nicely into a B4 envelope. If you fold this letter once to A5 format, then it will fit nicely into a C5 envelope.
- B and C formats naturally are also square-root-of-two formats.
The following table shows the width and height of all ISO A and B paper formats, as well as the ISO C envelope formats. The dimensions are in millimeters:
| A Series Formats | B Series Formats | C Series Formats | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4A0 | 1682 × 2378 | – | – | – | – |
| 2A0 | 1189 × 1682 | – | – | – | – |
| A0 | 841 × 1189 | B0 | 1000 × 1414 | C0 | 917 × 1297 |
| A1 | 594 × 841 | B1 | 707 × 1000 | C1 | 648 × 917 |
| A2 | 420 × 594 | B2 | 500 × 707 | C2 | 458 × 648 |
| A3 | 297 × 420 | B3 | 353 × 500 | C3 | 324 × 458 |
| A4 | 210 × 297 | B4 | 250 × 353 | C4 | 229 × 324 |
| A5 | 148 × 210 | B5 | 176 × 250 | C5 | 162 × 229 |
| A6 | 105 × 148 | B6 | 125 × 176 | C6 | 114 × 162 |
| A7 | 74 × 105 | B7 | 88 × 125 | C7 | 81 × 114 |
| A8 | 52 × 74 | B8 | 62 × 88 | C8 | 57 × 81 |
| A9 | 37 × 52 | B9 | 44 × 62 | C9 | 40 × 57 |
| A10 | 26 × 37 | B10 | 31 × 44 | C10 | 28 × 40 |
Think this will be help you to find the Intarnational Paper sizes...

No comments:
Post a Comment